0.1. Notice
Every style and image in this UI style guide is tentative. Nothing has been agreed upon or approved in any official manner.
Products are made to be used. There is no reason to add effort to develop, test, and document a product that won’t be used as much as expected. In software products the user experience is provided mainly through the user interface, and how a user interface is developed is guided by a UI style guide.
-
The purpose of this UI Style guide is to create a basis to have a consistent look and feel of the complete Evergreen web staff client.
-
The guide always emphasizes user-centered design.
-
It will be mainly used by developers without limiting anyone who needs to consult it.
1. Design Principles
1.1. Be Simple
Simplicity of tasks, white spaces, and an intuitive navigation are the perfect combination that users expect from a web application. Reducing extra effort avoids frustration and early abandonment.
Don´t
UIs become cluttered and complex when too much data is displayed; it can produce confusion and can make the application more difficult to learn.
Do
Design Patterns such as Progressive and Staged Disclosure can be applied. Focus is always on reducing user effort.
1.2. Be Concise
Users need their tasks to be done quickly and effectively. Give brief and precise instructions so users do not waste time completing unnecessary information or thinking too much about how to proceed.
Don´t
The user is discouraged when seeing that too much information must be completed.
Do
Account Registration Design Pattern can be applied. The less information required, the more satisfying the action will be.
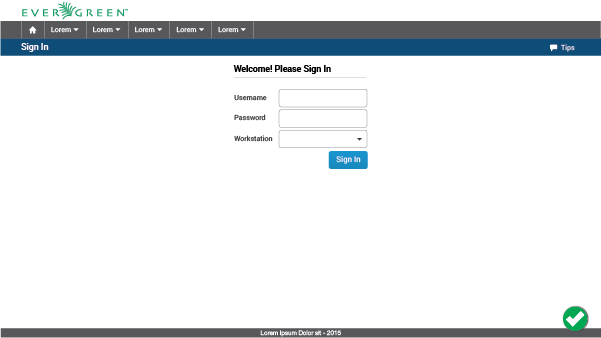
1.3. Be Consistent
Users feel lost when everything changes as they move around a web application. Visual consistency makes UIs easier to use, gives an overall impression of professionalism and reliability, and reduces the slope of the UI learning curve, which is one of the main “enemies” of the user experience.
Don´t
Changes between screens of the same application are evidence of missing guidelines.
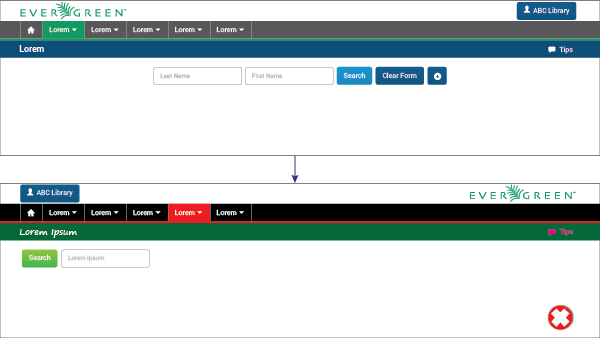
Do
Conventions are made to be followed. Preset guidelines ensure uniformity. The usability heuristic “consistency and standards” explains this.
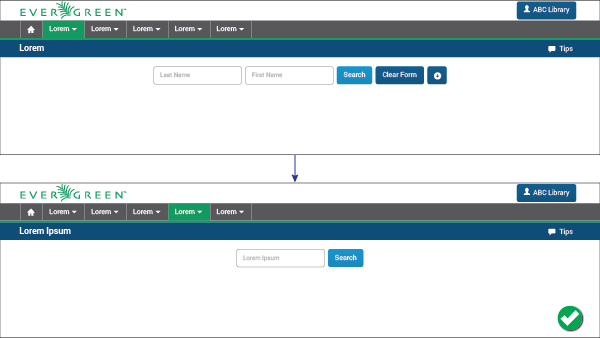
1.4. Give Continual Feedback
Feedback is an essential property of a usable product, and necessary to avoid confused or frustrated users. It is critical for the user to naturally flow through the UI without wondering what is happening. Notify the user that all actions he or she is performing are being processed, made, or verified at all times (as necessary).
Don´t
Users need to have control over the application. If it doesn´t respond as expected, they get impatient quickly and can end up frustrated.
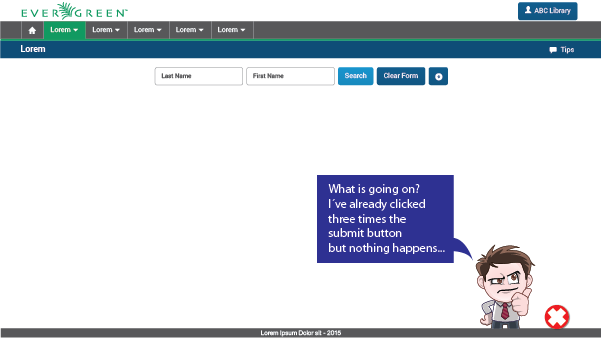
Do
A spinner can be an effective solution to avoid dissatisfaction among users. Suggestion: use visibility of system status (usability heuristic) to prevent these kinds of unresponsiveness issues.
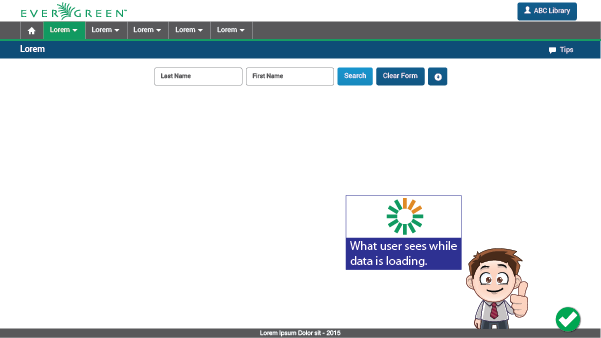
1.5. Being friendly always works
Language is the most important way to communicate between people, but communication channels and codes vary a lot when a system is involved. Show that systems are developed by people; avoid technical words or codes, and be gentle in the way things are stated.
Don´t
People who are not involved in the world of coding do not understand technical language commonly used by developers.
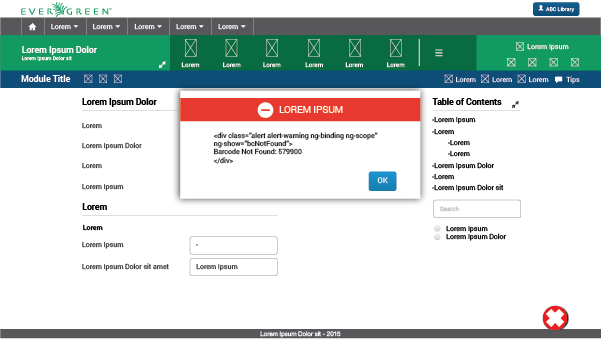
Do
Using simple, understandable, and kind language will be welcomed and appreciated by the user. Take into account the usability heuristic calling for a match between the system and the real world.
2. Page Layout and Structure
This section will provide the basic guidelines to develop a consistent user interface throughout the whole application. A consistent UI has the following benefits:
-
When designing, it removes the need to make the same decision repeatedly;
-
When coding, it enables the use of templates and pre-defined snippets of code;
-
It also gives the possibility to facilitate UI development to create a scalable application.
2.1. Metrics
Metrics were designed for three different screen resolutions. As the screen resolution increases, the measures change accordingly. These metrics have to be respected within the web staff client, where doing so will bring consistency, order, and a neat UI design.
All the metrics are going to be used for all the screen resolutions within each range. The base of each measure will be the typography size of the body. Metrics are expressed in "ems".
Besides the body, there are two additional sizes of typography in the UI design. The body typography will determine the UI measurements and the size of text within the majority of the web staff client. Where the two additional text sizes are used, UI metrics will still be maintained based on the typeface size of the body, and only the typeface size will change.
2.1.1. Ranges
1366 x 768 to 1600 x 1200
From now on "Range #1". Taking 16px as the default typography size of the body, 1em is going to be equal to 16px always.
1600 x 1200 to 1920 x 1080
From now on "Range #2". Taking 18px as the default typography size of the body, 1em is going to be equal to 18px always.
1920 x 1080 to 2560 x 1440
From now on "Range #3". Taking 20px as the default typography size of the body, 1em is going to be equal to 20px always.
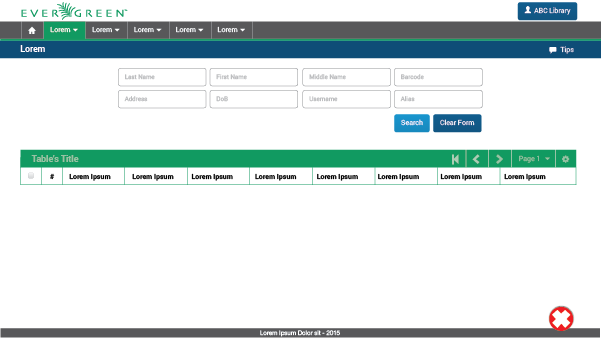
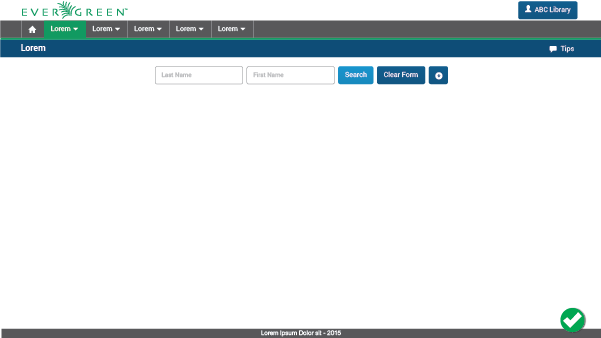
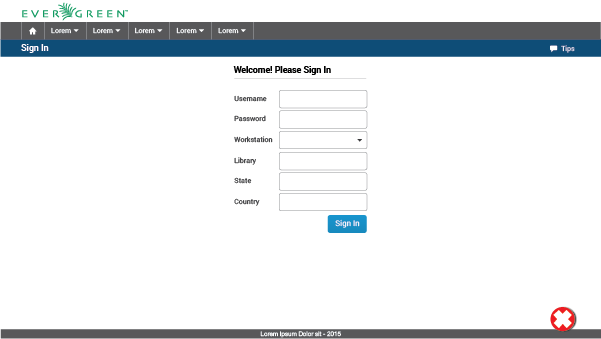
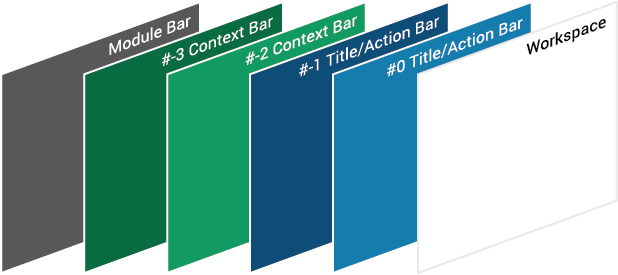
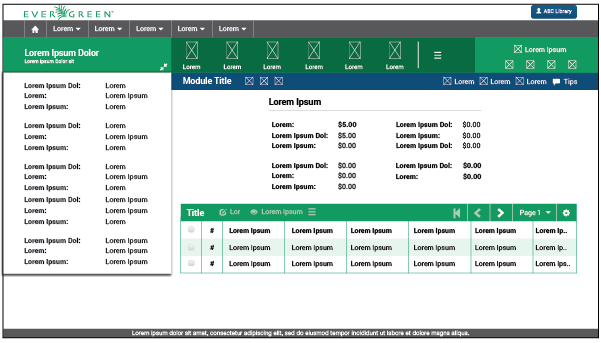
2.2. General Page Structure
The UI general structure is divided into two types of user interfaces depending on the information displayed. This difference is defined by the presence or absence of context. Context is understood as an entity with a given state to which a set of actions can be applied and, in consequence, modify its state.
2.2.1. Without Context
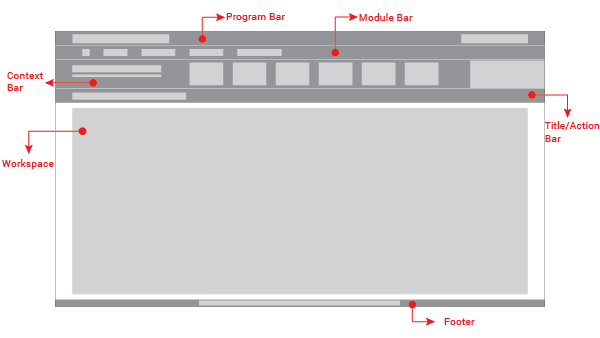
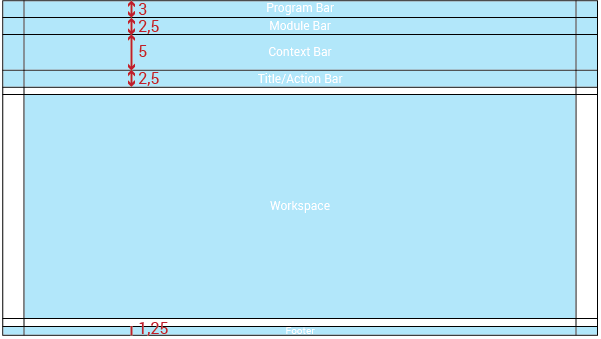
The UI without context will be composed of five main elements:
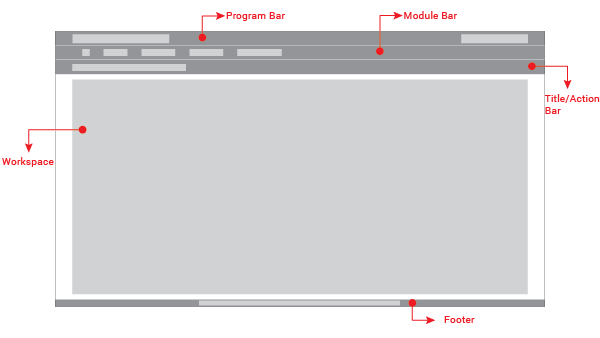
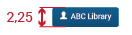
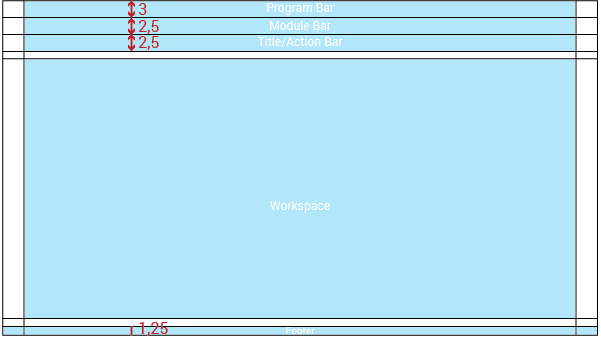
Program Bar: It is important for the project to locate its logo permanently within the web application so that users know where they are even though it is a tool used often. This section will always be located at the very top of the page. Evegreen’s logo will be located on the left side. It also shows a user/library button that will allow the user to log out, switch between different accounts, apply configuration options, or perform any other action related to the user’s account. This button is located on the right side of this header.

Metrics
The program bar will have a height of 3em and its width will be adapted to the screen resolution width. Margins will be 3em.

Evergreen´s logo will be:

The user/library button will be as large as the text is; also the distance between the icon and the text is measured and has to be respected (see more in "Buttons" - Visual Design):
Module Bar: All the actions that can be performed across the web application are divided and grouped into modules. Those modules are located in this bar present in all the web app screens. When clicking the modules, a dropdown menu will be displayed. The bar can contain as many modules as needed.
Metrics
The module bar will have a height of 2.5em and its width will be adapted to the screen resolution. Margin will be 3em.

There are some metrics that are important to respect in the module bar structure like the distance between the text and the down arrow and the distance between each module title:
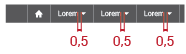
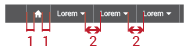
Each module is separated by a thin white line that will make each module work like a button.
Title/Action Bar: The user must be able to easily locate the title of the current module activity. This bar will contain the activity title in left alignment. This bar is also able to handle tabs, and sometimes contains buttons. The bar’s overall purpose is to locate the user and trigger actions that apply to the entire page. The Title/Action Bar will stick to the top of the screen as the user scrolls.
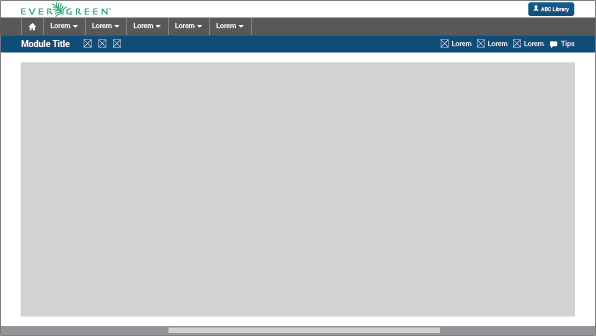
Metrics
The activity title’s font size will be in Range #1: 20px bold; in Range #2: 22px bold; and in Range #3: 24px bold. Every title will be left aligned with a left margin of 3em.
Action buttons will be located on the right side (respecting the 3em margin) or next to the title.


Tabs are elements where the content is separated into different panes, and each pane is visible one at a time. The user requests content to be displayed by clicking the content’s corresponding tab control. When functioning as a tab bar, each tab’s title type will measure the same as the body’s typography size in the regular weight. Each tab will be separate by a thin white line.

Workspace: The information should be presented consistently in all the different screens of the web application. Variable content (text, forms, lists, tables, etc) will be shown only in this limited area. Margins and grids must be respected.
Metrics
Some metrics that need to be respected are the distance between the workspace and the bar above it and the footer below it (1em). Also, both sides have 3em margins.
Footer: The fact of Evergreen being an open source software project should be communicated to the user. The footer will contain a brief description about the license used and also the most recent release year to show that it is regularly updated.
The text will be 14px (Range #1)/ 16px (Range #2)/ 18px (Range #3) and will be aligned to the center of the footer:

2.2.2. With context
The general structure is the same with and without context, the only difference is that a new bar is displayed. The UI with context will be composed of six main elements:
Context Bar: This bar will appear only when an action set could be applied to a specific context. The actions will be represented with icons from the FatCow icon set.
Metrics
The size of typography varies with respect to the body only in the left section (where the context is mentioned). Every context will be written in 20px bold, while the subtitle type size is 14px. This subtitle will express some important details that are relevant to users.

The icon region requires some explanation:
-
The main icon set used is "FatCow", width = 2em.
-
The maximum number of icons (with their respective entries, and including the hamburger icon) is seven.
-
Icons set must be left aliged.
-
The presence of the hamburger icon (in the right side of the context bar) represents that there are more possible actions beyond the six shown.
-
If the number of actions that can be performed to the context is fewer than eight, the hamburger icon will not be displayed.
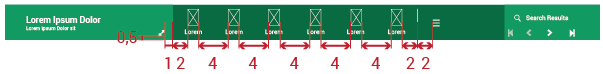
In the right portion of the context bar we can find a section called the "Results Manager". It allows the possibility of returning to the UI where the search results are, going to the next or previous context one by one, or to the first or last one directly. It also gives the option of searching a new context. It will be displayed only when the context is arrived at from a search interface.

2.3. Layout template or grid
The layout template or grid will be orthogonal. This template will be adapted (scalable) to different screen resolutions. With context:

Without context:

2.3.1. Metrics
Horizontal margin will be 3em on both sides of the UI.

The general structure is divided into three main columns. These columns define the location of the content in the workspace. There are secondary baselines that create a smaller subarea if neccessary.
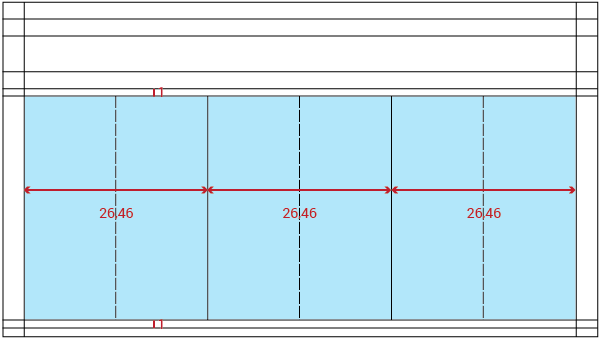
Depending on the presence or absence of context the workspace region will vary. With context:
Without context:
2.3.2. Popups metrics and structure
Metrics apply to all types of popups. Their structure:
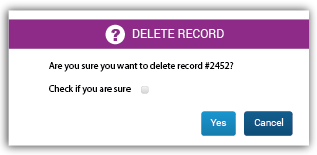
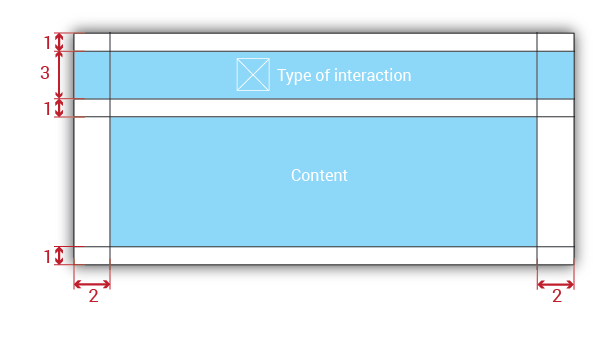
Popups will be divided into two areas:
-
Title Bar: This bar will contain an icon from the Glyphicon set (with width = 2em) illustrating the type of interaction, followed by the title of the message displayed. In addition, this bar will have different colors depending on the information it handles.
-
Content Region: The message itself will be contained in this area. The message will be expressed by text, UI elements, or both. Messages will be accompanied by buttons which will accept or cancel them.
2.3.3. Types
There will be five different types. The major difference between them will be the title´s background color and its icon:
-
Error: When something isn’t going as expected, an error occurs or the information introduced is wrong, an error message popup will be displayed. The title’s background color is wrong red.

-
Information message: The only purpose of this kind of popup is to inform. Its title’s background color will be informative blue.

-
Success message: Displayed when a user-requested action has been successfully completed. Title’s background color: positive green.

-
Question message: Sometimes the system will need a confirmation or information from the user to perform a specific action or process. Title’s background color: insecure purple.

-
Action Alert: This modal alert will provide additional fuctionality to the system by displaying a popup requiring the user to perform an action. The title’s background color is active brown.

3. Visual Design
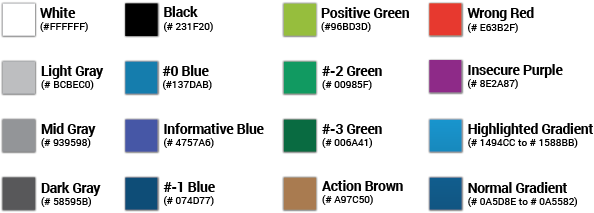
3.1. Color
A color palette summarizes all the colors used across the web application. Each color was selected carefully to work harmoniously with one another. They are also grouped conceptually into hierarchical layers. There will be an order that has to be applied to the different layers in the web app, creating a scale from the less important to the most relevant information. This hierarchical order is used by the general structure, and the concepts have also been applied such that elements in the workspace can (in most cases) simply follow the colors established in the UI Elements guidelines.
3.1.1. Color Palette
This is the general color palette of Evergreen’s web staff client:
3.1.2. Color Layers (Structure)
Colors give hierarchy to elements. The color combination establishes logical layers that imply the visual importance of each element, guiding the users' eyes to what is more relevant in the UI.
Establishing a fixed and well defined visual hierarchy using colors, but only at a structural level, ensures a precise visual order of the information displayed and eliminates potential problems of consistency and subjectivity.
3.1.3. Color Meanings (Popups)
In special cases, colors can give meaning to elements. Each color has a meaning, and should be applied to elements that need to transmit an implicit message. This approach is used primarily in popups or dialogues, ensuring that both the tone and the message will be emphasized by using a visual resource.
-
Wrong Red: This red is used to inform the user that something is wrong.
-
Positive Green: Positive means that a specific task was achieved as expected, or that there are no problems.
-
Informative Blue: This blue is used just to inform users of something.
-
Insecure Purple: When something needs an answer of any kind, insecure purple appears.
-
Action Brown: Color that has to do with performing an action.
-
Grey Scale: These three greys are used to guide users.
*Refer to the color palette to relate colors to explanations.
3.2. Typography
Roboto is a font extensively tested in many devices. It guarantees legibility, clarity, and readability.
Evergreen will use this typography only in two weights: regular and bold. Every text will be written in regular, titles of modules and contexts will be in bold.

As mentioned before (Page Layout and Structure - Metrics), the guide supports three screen resolution ranges. There are three different text sizes used within each range; here is a table showing where to apply each size related to the range:
1366x768 to 1600x1200 |
1600x1200 to 1920x1080 |
1920x1080 to 2560x1440 |
|
General Type size (body) |
16px |
18px |
20px |
Context Title |
20px |
22px |
24px |
Subtitle’s Context |
14px |
16px |
18px |
Title’s Actions (Context Actions) |
14px |
16px |
18px |
Title (Title/Action Bar) |
20px |
22px |
24px |
Tabs (Title/Actions Bar) |
16px |
18px |
20px |
Footer |
14px |
16px |
18px |
3.2.1. Type color
-
When the background color is white or a light color: Roboto Normal 400 will be dark grey (#231F20).
-
When the backgrund color is a dark color: Roboto Normal 400 will be in white (#FFFFFF).
You can download Roboto Normal 400 from: Google Fonts
3.3. Iconography
There are two types of icons used in the web staff client: Bootstrap Glyphicon Halflings set and FatCow Icon set.
Bootstrap Glyphicon Halflings set will be use in the whole web staff application.
FatCow Icon set will be use in the Context Bar to illustrate each action that can be applied to a particular context and in the home page.
4. UI Elements
A single UI design contains a wide variety of components such as buttons, lists, forms, menus, and tables.
By giving them a guideline to follow, designers and developers will achieve consistency. These elements can be divided into three groups:
-
Input Controls: These elements involve data input, modifications, and calls to action.
-
Navigational Components: Elements that help the user to locate and understand the path between the different user interfaces of the application.
-
Informational Components: These enhance the organization and clarity of the information provided in the screens.
Users have become familiar with elements acting in a certain way, so choosing to adopt those elements when appropriate will help with task completion, efficiency, and satisfaction.
4.1. Input Controls
4.1.1. Buttons
Buttons are a stylized text or image that illustrate an action and invite the user to click it. There are three types of buttons:
-
Primary Button: This button will be the most used, alone or accompanied by other types of buttons.
-
Accent Button: Used jointly with the primary button to create a noticeable difference between buttons.
-
Flat Button: This type of button is not outlined by a background. It is used mainly in structural bars.
Specs
Primary buttons will be:
-
Font
-
Roboto Regular.
-
Font size: 16px (Range #1), 18px (Range #2), 20px (Range #3).
-
Font color: white (#FFFFFF).
-
-
Background
-
Rectangle with a 5px corner radius.
-
Lineal Gradient from # 0A5D8E to # 0A5582.
-
Light will always be at the top of the button.
-

Accent buttons will be:
-
Font
-
Roboto Regular.
-
Font size: 16px (Range #1), 18px (Range #2), 20px (Range #3).
-
Font color: white (#FFFFFF).
-
-
Background
-
Rectangle with a 5px corner radius.
-
Lineal Gradient from # 1494CC to # 1588BB.
-
Light will always be at the top of the button.
-

Flat buttons will be:
-
Font
-
Roboto Regular.
-
Font size: 16px (Range #1), 18px (Range #2), 20px (Range #3).
-
Font color:
-
On a white background: Dark gray (#231F20).
-
On a color background: White (#FFFFFF).
-
-

Button Content
Buttons of any type can contain only text, only an icon (Bootstrap Glyphicon Halflings set) or both. They can also function as a dropdown menu trigger. Here are the possible combinations (for both, with background and flat buttons):

Metrics
All buttons will have fixed heights, while the width will vary according to the word or icon each button contains.

As said, text will be 16px (Range #1), 18px (Range #2), 20px (Range #3) in a center alignment. Margins will be 1em.
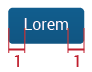
If the button is a combination of text and an icon:
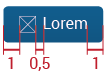
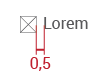
If the button contains only an icon:
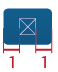
If the button functions as a dropdown trigger:
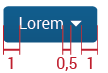
Distance between buttons:
State
Not pressed:

When pressing:

Gradient will be eliminated, so the background color will change to:
-
Primary Button: #003354
-
Accent Button: #0B6A93
-
Flat Button:
-
On a dark color background will be white in both states.
-
On a light / white background will be dark gray in both states.
-
Disabled:
When a button is not available it will look like:

This is achieved by applying opacity=0.5 to the text/icon/both in primary, accent and flat buttons. In the first two the background will retain its color as established.
4.1.2. Checkboxes
Checkboxes allow the user to select one or more options from a set. Checkboxes should be located:
-
At the right side of a word if it is the only option that the user can check

-
At the left side of a set of options if the user can perform a multiple selection

-
Alone. They will be visually separated from the text; however, they correspond to a specific option.

The default input type="checkbox" should be used to apply this element to the UI. Every checkbox will be located 1em from the word (to the left or right side) or in a center alignment.
State
Unchecked:

Checked:

4.1.3. Expand/collapse
When there is lack of space, or there is information that can be hidden momentarily to perform other actions yet remain easily accessible, this concept should be applied. This control is illustrated by an icon from the Bootstrap Glyphicon Halflings set:
-
glyphicon-resize-full:

-
glyphicon-resize-small:

The icon will have 1em of width. Its color will vary depending on the backgruond color: if the background color is white or a light color, use #231F20 (dark gray); if the background color is a dark color, use #FFFFFF (white).
The way in which the information is shown when expanding should vary depending on the place the icon is located.
Inside a bar:
Information will be within a white rectangle with a faint shadow around it. Notice that the content in the workspace is not covered; it was adjusted to fit in the remaining space.
In the workspace:
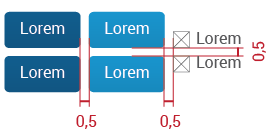
4.1.4. Dropdown Menu
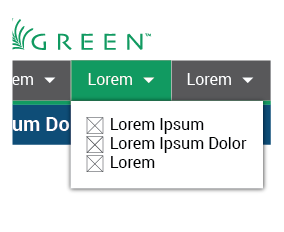
Dropdown menus allow the user to select an item at a time and perform different activities. It is also a way to save space. There are two types:
-
With selection icons: Used when the selections are primary actions. These actions will generally result in a new interface being displayed.
-
Without icons: Used to display secondary actions. Such actions are applied to a specific element and may therefore change the contents of the screen, but will not result in a new interface.

Specs
-
Font
-
Roboto Regular.
-
Font size: 16px (Range #1), 18px (Range #2), 20px (Range #3).
-
Font color: Dark gray (#231F20).
-
-
Background
-
White background.
-
1px Shadow around the rectangle.
-
-
Icons (if needed)
-
Width=1em.
-
Color: dark gray (#231F20).
-
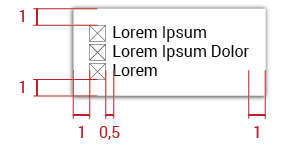
Metrics
There are no specific measurements for the menu size; it will depend on the content of each dropdown menu. But metrics do determine with margins between objects:
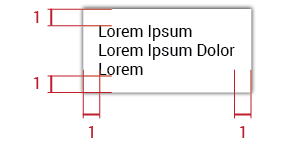
4.1.5. Date Pickers
When pickers are used to select a date, the information is consistently formatted and input into the system.
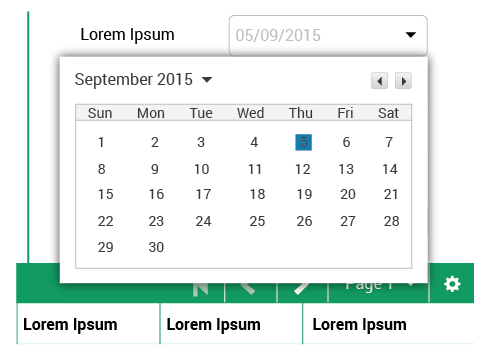
The picker will be composed of a calendar of the current month and toggles to select different months.
Metrics
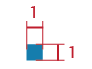
The picker itself will be # 0 Blue (# 137DAB), and its measure will be 1em square:
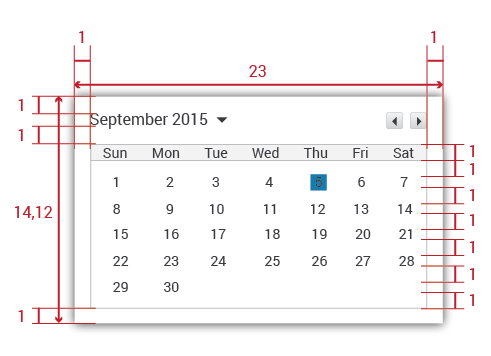
In context:
4.1.6. Toggles
Toggles allow the user to cycle through options one by one. The arrow pointing to the left symbolizes going backwards; the arrow pointing to the right represents going forwards. There are two different types:
-
Common toggle: Illustrated by two little buttons with a left and right arrow within each background.
-
Tips toggle: Its structure, metrics and specs are the same as flat buttons, the difference is that in a normal state means it is inactive and when it is yellow means it is active. This type of toggle is applied to a specific action: tooltips in the UI. It is located on the right side of the title/action bar.
Metrics
Common toggles will measure:
Each arrow will be center aligned. They will measure:

Tips toggles will measure:

States
Tips toggle inactive (by default):

Tips toggle active (by clicking it):

4.1.7. Text fields
Text fields allow users to enter data. They can allow either a single line or multiple lines of text. There are different types.
Specs
-
Font
-
Roboto Regular.
-
Font size: 14px (Range #1), 16px (Range #2), 18px (Range #3).
-
Font color: Light gray (# BCBEC0).
-
-
Background
-
Rectangle with a 5px corner radius in dark gray (# 231F20).
-
No Gradient.
-
White background color.
-
-
Icon (arrow - dropdown field)
-
Width = 1em.
-
Color: dark gray (#231F20).
-
Metrics and Types
Single line:

Text fields with a single line can have a help text to guide the user to enter the correct information in them. The text will be 1em from the left border:

Multiple lines:
These metrics are defined as a default. The text field would have the possibility of being manually resized according to the user needs (with the resize handle represented in the bottom right corner).

Dropdown Field:
When users can choose between a set of options, a dropdown field will be displayed.

Toggle Field:
This type of text field allows users to cycle through consecutive options, giving the possibility of going backwards and forwards.

Distance between fields:
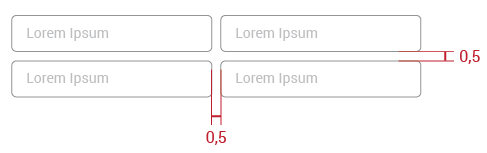
States
Default: When the text field is in its default state, it will look like:

Filled: Once it is completed or the option is selected (in the dropdown or toggle field types), it will look like:

The difference is the text color: light gray (# BCBEC0) turns into dark gray (#231F20).
Clarification: In the multiple lines text field, the text will be written always in dark gray (#231F20). It doesn´t have different states.
4.1.8. Forms
Forms allow a user to enter data which is sent to a server for processing. They can also be used to retrieve information from a server. They are composed of labels, text fields, and buttons, though in some cases, the labels can be omitted.
Specs
-
Text Font (label)
-
Roboto Regular.
-
Font size: 16px (Range #1), 18px (Range #2), 20px (Range #3).
-
Font color: dark gray (# 231F20).
-
-
See text fields specs
Metrics and Types
Single Row: When only one or two fields are needed to perform a specific action, they may be displayed in a single row. In such cases, help text may be placed within the field to guide the user in lieu of a label. Distance between fields and buttons will be 0.5em.


With Label: A label should be used next to each text field when the form requires three or more fields. That label will be the indication of the information to enter in the text field. Labels are left aligned to facilitate scanning for a particular field. Help text inside the text field can work as an example of what to introduce or to specify that the field is required or optional. It is not neccessary to use it in every case, but only when additional clarity is required.
In forms of three or more fields, the fields will be arranged into a single column. Buttons are located at the bottom of the form in a right alignment.

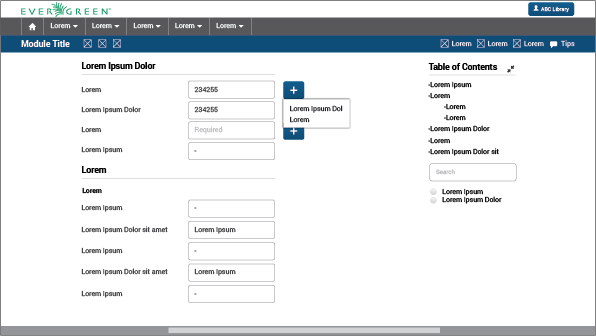
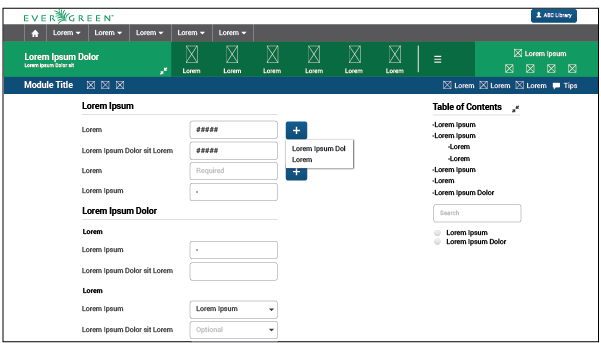
Large forms: Forms that are divided into more than one related sections are called large forms. They are composed of subheaders, lables, text fields, and sometimes buttons. (Remember: if forms or other large UI elements occupy the entire workspace, actions that are applied to it (i.e. the entire page) should be located in the title/action bar.)
Large forms need space, so they are located in the workspace and are not accompanied by any other content due to the large number of elements involved in the page. They are presented in a single column. Metrics of fields, subheaders and labels are:
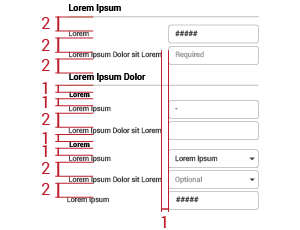
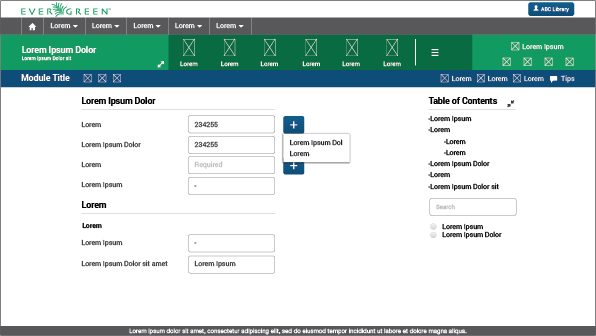
There are a table of contents, a search field, and some filters to the upper right of the large form. Those elements help users find specific fields, or manage the visualization of needed fields. It is most useful when forms are too large and exceed the height of the screen. By clicking each item in the table of contents, users can get to that specific portion of the form.
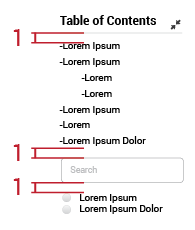
4.1.9. Radio Buttons
Radio buttons are used when you want to let users select one - and just one - option from a set of alternatives. Every radio button will be located 1em from the word (left or right side) or in a center alignment.
When there is only one option the radio button will be located at the right side of the text:

When there are more than one option, the radio button will be located at the left side of the text:

State
Unchecked:

Checked:

4.2. Navigational Components
4.2.1. Network Indicator Activity
Feedback is a very important source to use in user interfaces. Users need to know what is happening with every interaction they make. A spinner will let the user know that the system is working, which avoids frustration.
The network indicator activity element will be composed of a spinner, a message, and will be shown as a popup.
Specs
-
Font
-
Roboto Regular.
-
Font size: 16px (Range #1), 18px (Range #2), 20px (Range #3).
-
Font color: Light gray (# BCBEC0).
-
-
Background
-
White color rectangle.
-
Shadow around the rectangle´s perimeter.
-
-
Spinner colors
-
Green (# 00985F).
-
Orange (# F7941E).
-
Metrics
The alert will measure:

The spiner will be:
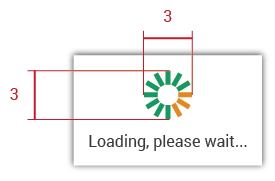
Effect
The spiner will have an effect of clockwise rotation. The three orange rectangles will be moving around the green ones until the action or activity is ready:

4.2.2. Menu Selector
This element helps users know where they are by highlighting the pane of a menu or tab displayed on the screen. It is going to be adapted to the different sizes of menus or tabs. This UI element will also add a 4px border to the bottom of the highlighted row.
Specs
-
Colors
-
# -2 Green (# 00985F).
-
# 0 Blue (# 137DAB).
-
-
Shape
-
Rectangle.
-
Straight edges.
-
-
Size
-
4px of height, screen width.
-
Metrics
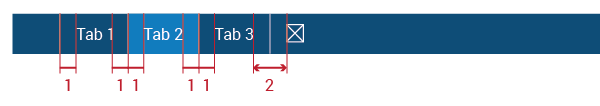
Menu selector metrics will vary according to where they are. In menus, they will have the menu´s height and margin=1em; in tabs, the tab´s height and 0.5ems of margin on both sides:
Module Bar:
Context Bar
Title/Action Bar (Tabs):
States
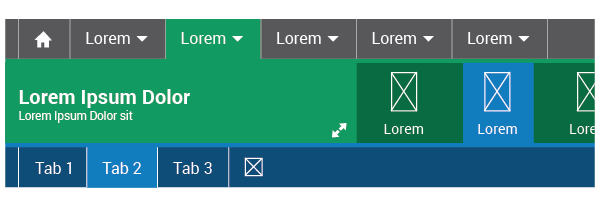
Selected:
On hover over:
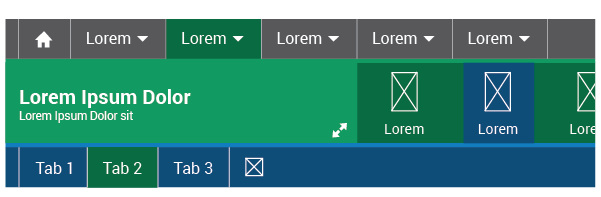
On hover over the color changes to:
-
Module Bar: # -3 Green
-
Context Bar: # -1 Blue
-
Title/Action Bar: # -3 Green.
4.3. Informational Components
4.3.1. Tool Tips
A tooltip allows a user to see hints when they hover over an item indicating the name or purpose of the item.
Specs
-
Font
-
Roboto Regular.
-
Font size: 14px (Range #1), 16px (Range #2), 18px (Range #3).
-
Font color: Dark gray (#231F20).
-
-
Background
-
White color rectangle.
-
Shadow around the rectangle´s perimeter.
-
-
Margin
-
1em in both left and right sides, from the border to the text.
-
-
Metrics
-
Will vary depending on the text. It can contain a single line or multiple lines. It measures can not be greater than width=12.5em and height=10em or less than height=2.25em.
-


4.3.2. Dividers
Dividers are thin gray lines that help divide spaces or regions of the UI to organize and make the information display more clearly.
Specs
-
Line
-
1px thickness.
-
Mid gray color (#939598).
-
-
Location
-
Workspace
-
Dropdown Menu
-
Forms
-
Alerts
-
-
Usage
-
To separate different items within a set.
-

4.3.3. Subheaders
Subheaders function as subtitles within a module. They are located only in the workspace and alerts. There are two types:
-
Primary Subheader: A combination of text and divider.
-
Secondary Subheader: Bold text.
Specs
Primary Subheader:

-
Font
-
Roboto Bold.
-
Font size: 20px (Range #1), 22px (Range #2), 24px (Range #3).
-
Font color: Black.
-
-
Location
-
Workspace
-
Alerts
-
-
Usage
-
To separate different content within a UI.
-
-
See divider specs.
Secondary Subheader:

-
Font
-
Roboto Bold.
-
Font size: 16px (Range #1), 18px (Range #2), 20px (Range #3).
-
Font color: Black.
-
-
Location
-
Workspace
-
Alerts
-
-
Usage
-
To separate different content within a UI once the primary subheader is already applied.
-
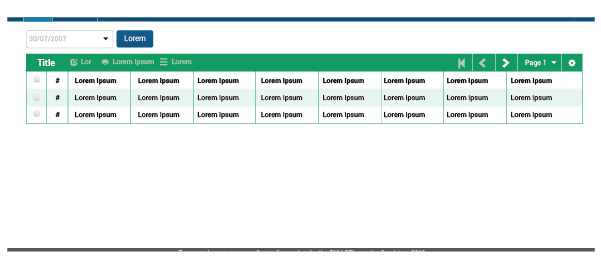
4.3.4. Tables
The table UI element is one of the most frequently used within the Evergreen web staff client. It retrieves required information and shows all the results in an orderly way. Tables are resizable; they adapt to the whole screen width or to the remaining space in the workspace. One can also resize the default width of individual columns.
Structure
Tables are composed of three main areas:

-
Table Bar: This bar contains a wealth of information and features for every table. It will show a title to locate the user; an Action set which can be applied to the rows; a Page navigator to work through the set of information; and a Table configuration icon (cog icon) to change the default table view and other configuration options that apply to every table.

Something important to highlight is the action set. It is composed of up to three buttons; the first two will be the most common actions, and the third is a trigger button to open more actions (shown as a dropdown menu).
-
Columns Bar: This section will display the a "Check all results" checkbox to implement a specific action - or set of actions- on all the results retrieved, a "Number of result" column to facilitate the observation of information, and the column headers for each field being displayed.

-
Table Results: Where all the results retrieved are exposed. The information will be presented according to either the default configuration or options selected by the user.
Metrics
Table bar: Height of 2.25em. #-2 Green background color. Each icon used in this bar will have width=1em.

Columns Bar: Height of 2.25em.
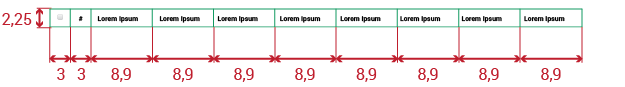
Table Results: Each row will have 2.25em of height. As a visual detail, every other row should have a #-2 Green background color with opacity=0.2 to help the visualization of the information, starting from the first row. The number of columns will always be 8 (without the number of column and the checkbox columns) as a default.

Results States
Table results have two posible states.
Default: Checkboxes are unchecked and the actions set is disabled.

Selected: One or more checkboxes will be checked and the actions set will be enabled.
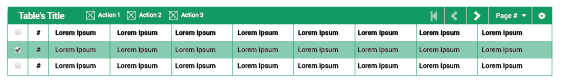
Combination
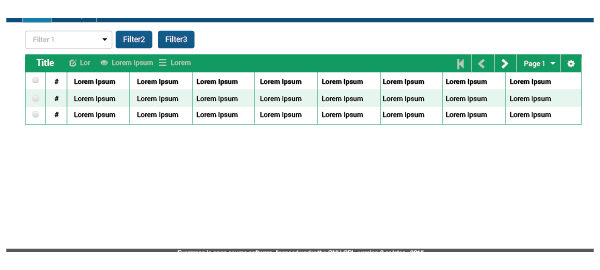
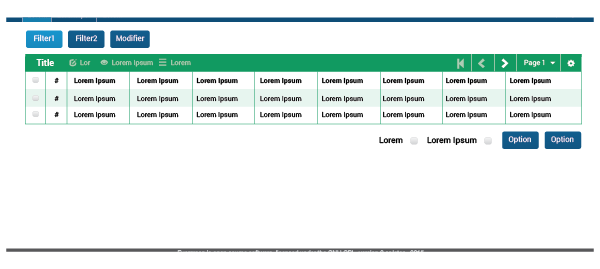
One common combination will be buttons/checkboxes/text fields + table. Buttons can work as filters to the table, as an in-page menu, as a way to change the table’s results, or as a modifier. They should be located above the table so the user can see them quickly and know the possibilities, and because options at the bottom may end up off the screen. There can be cases in which buttons or checkboxes are placed at the bottom of the table, but this should happen only when more than three options are required:
Up to three buttons:
More than three buttons:
Grouping
When a specific UI element (or combination of elements) is completely related to a table, and is displayed in conjunction with elements not directly tied to the table, the related element (or elements) should be grouped with the table by a thin line. The line will be 1px, with a 5px rounded edges only in the upper corners, in a #-2 Green color.
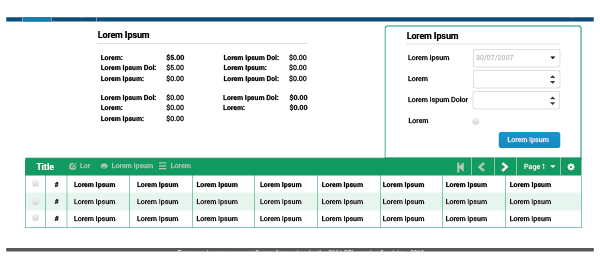
When there is no more information displayed on the screen than the table and the related UI element (or combination of elements), is not neccessary to group them with a line.